Nuclear fuel cycle is a whole process of obtaining, using, processing and recycling the nuclear fuel. It generally includes uranium resource development and nuclear fuel processing (front end), usage of nuclear fuel in the reactor and spent fuel processing (rear end). The reactor is a central link of nuclear fuel cycle, and the fuel component is the heart or core of the reactor.
Schematic Diagram
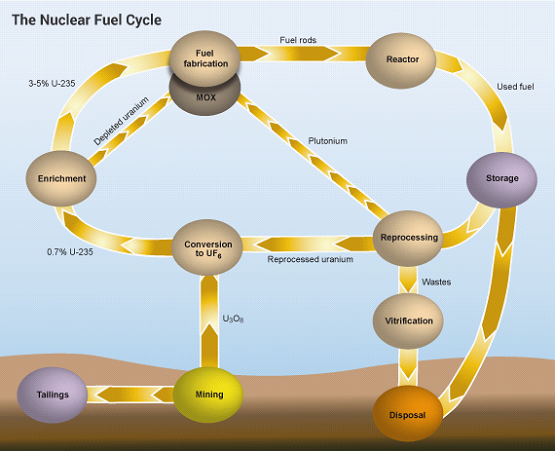
Front end
Ø Uranium ore geological prospecting
Uranium is the most basic raw material of the nuclear industry. The geological prospecting task of uranium is to find out and study the geological condition to form the uranium deposit, expound its time and spatial distribution rules, apply its formation and distribution rules to guide prospecting and exploration, and prove the underground uranium resource.
Uranium in the crust exists in the form of uranium mineral, isomorphism (uranium bearing mineral is formed) and adsorbed state. For active chemical properties of uranium, there is no natural pure element. The uranium mineral is mainly used for forming the compound. At present, there are more than 200 kinds of uranium minerals and uranium bearing minerals, only more than 10 of which have practical mining values.
The uranium deposit is an accumulation body of the uranium minerals. The uranium deposit is formed by constantly integrating uranium elements in the crust under various geologic processes, and consistently evolving the crust. It is of great significance to find out the forming process of uranium deposit and effectively guide, prospect and explore.
The uranium prospecting and exploration process includes regional geological survey, prospecting and detailed survey, reveal and evaluation and exploration, all of which are interconnected. Meanwhile, it is also accompanied by a series of fundamental geological work, covering topographic survey, geological mapping, raw data logging, rock mineral identification, chemical and physical analysis for sample, ore process test, etc.
Ø Uranium mining
Uranium mining is the first step to produce uranium. The task is to explore the industrial uranium ore from the subterranean deposit, or chemically leached to obtain a liquid uranium compound. Mining of uranium and other metal substances is essentially the same, but uranium can emit radioactive gas (radon gas) for its radioactivity. With low grade, dispersed ore body and complicated form, uranium mining has some special places.
Uranium mining method mainly includes open-pit mining, underground mining and in-situ leach uranium mining
Ø Uranium extraction process (hydrometallurgy)
The basic task of uranium mining extraction process is to process and enrich the mineral resources into intermediates with high uranium content, which are generally called chemical uranium concentrate, and further strengthened and processed to be uranium oxide as a raw material for next process.
The conventional uranium extraction process generally includes ore grade, ore grinding, ore leaching, solid-liquid separation, uranium extraction (purification), precipitation, etc.
After mineral resources are extracted, uranium minerals are fully exposed to be leached after being crushed and ground; and then valuable ingredients are selectively dissolved out by some chemical reagents and other means under a certain process condition. There are two leaching methods: acid process and alkaline process.
The ore pulp leached from the ores contains ore tailings. Such common methods as filtration, centrifugation and precipitation are applied to separating solids (leached tailings) and liquid (leaching agent) by virtue of a certain method. Dilute ore pulp or clear solution may be obtained with the help of solid-liquid separation.
With low uranium content, diversified impurities and high content, the nuclear power station requirements can be achieved by removing these impurities. Ion exchange method (also called adsorption method) and solvent extraction method can be provided for solution purifying process. The process engineering of setting chemical uranium concentrates is the last process of hydrometallurgy process. The precipitation method includes neutralizational process and hydrogen peroxide precipitation method. The precipitate is washed, filter-pressed and dried to obtain the hydrometallurgy product - chemical uranium concentrate (also called yellow cake).
Ø Uranium enrichment and production technology
According to different relative atomic masses of U-235 and U-238, uranium isotope is separated to form a more enriched U-235, which means enrichment. Gas diffusion process, gas centrifuge process and laser separation process are applied as the enrichment methods in the modern industry. Enrichment is conducted in the form of uranium hexafluoride. The separated tailings mean materials in which depleted uranium containing 0.3% of U-235 can be served as the depleted uranium bomb.
Ø Fuel element for the reactor
After purification or isotope separation, uranium cannot be directly used for nuclear fuel, but shall be chemically, physically and mechanically processed to obtain elements with various shapes and grades in complicated and severe manner. On this basis, it can be used as the fuel for varied reactors. This is a key link to ensure safe operation of the reactor. It may be divided into metal, ceramic and diffuse according to the component features, divided into columnar, rodlike, annular, tabular, strip-shaped, spherical and prismatic based on geological shape, and divided into elements of test reactor, production reactor and power reactor on the basis of reactors.
A great variety of nuclear fuel elements generally consist of fuel core body and cladding tube. The nuclear fuel element is composed of fuel component and the related components. The fuel component is used for releasing energy with the aid of fission. The related components include control rod, burnable poison, neutron source and choke plug, all of which play their respective role in controlling the chain reaction.
With severe operating condition in the reactor, the nuclear fuel element is in the environment with intense radiation, high temperature, high flow rate, even high pressure for a long time. Hence, the core has an excellent comprehensive performance. The small thermal neutron absorption section (except for the fast reactor) is further required for the cladding material, but cannot be damaged during the service life. Hence, it is a high technology to manufacture the nuclear fuel element.
Ø “Burning” of fuel element in the reactor
The nuclear power station is a power facility which uses heat energy generated by one or more power reactors for powering or powering and heat supply. The reactor is key equipment of nuclear power, in which chain reaction is conducted. The nuclear fuel element generates a good deal of heat for fission in the reactor; the heat is taken out by virtue of water in high pressure; steam generated in the steam generator propels the steam turbine to drive the generator to rotate; finally, electricity is constantly generated and delivered from near and far by the power grid.
Rear end
The nuclear fuel rear end includes storage in the reactor, transportation, intermediate storage, post-treatment (recycling) and permanent geological disposal of the fuel element (means spent fuel).
The spent fuel refers to fuel discharged from the reactor after reaction. It cannot be directly post-treated, but stored and intermediately stored in the reactor for a period of time to achieve a cooling aim.
Regarding different management measures for the spent fuel discharged from the reactor, there are mainly two strategies:
Ø One pass. The discharged spent fuel stored and intermediately stored in the reactor is delivered to the deep geological stratification for disposal or long-term storage as the waste after being directly packaged (or cut).
Ø Closed cycle. The nuclear fuel use process is subject to closed cycle after a series of post-treatment processes of the cooled spent fuel.